
In 1968, George Stigler defined an entry barrier as "A cost of producing that must be borne by a firm which seeks to enter an industry but is not borne by firms already in the industry." McAfee et al. criticized this as being tautological by putting the "consequences of the definition into the definition itself." Bain used the definition "an advantage of established sellers in an industry over potential entrant sellers, which is reflected in the extent to which established sellers can persistently raise their prices above competitive levels without attracting new firms to enter the industry." McAfee et al. McAfee, Mialon, and Williams list seven common definitions in economic literature in chronological order including: This has caused there to be no clear consensus on which definition should be used. Various conflicting definitions of "barrier to entry" have been put forth since the 1950s. In other cases it can also be due to inherent scarcity of public resources needed to enter a market. Governments can also create barriers to entry to meet consumer protection laws, protecting the public. First of all it is important to identify that some exist naturally, such as brand loyalty. Barriers to entry often cause or aid the existence of monopolies and oligopolies, or give companies market power.īarriers of entry also have an importance in industries. īecause barriers to entry protect incumbent firms and restrict competition in a market, they can contribute to distortionary prices and are therefore most important when discussing antitrust policy. For example, eBay and Amazon have broken geographical barriers by opening markets for many entrepreneurs in areas far from home.In theories of competition in economics, a barrier to entry, or an economic barrier to entry, is a fixed cost that must be incurred by a new entrant, regardless of production or sales activities, into a market that incumbents do not have or have not had to incur.

The Internet has reduced the barriers to entry in many industries. Entrepreneurs may choose to enter a business if they see another company earning a large profit. High barriers to entry benefit a company already in an industry by discouraging competition. Low barriers to entry foster increased competition by increasing the number of sellers. Government imposed trade barriers such as tariffs, quotas, and subsidies may prove to be too much of a barrier for a company to conduct business in a country. Other companies may be deterred from developing competing products. A company owning a patent creates a barrier since it has the exclusive right to manufacture a good or offer a service. Licensing and educational requirements restrict the number of professionals in many fields. Government regulation may also act as a hurdle to enter an industry. It would take even longer to generate the trust and loyalty required to survive. Other barriers include regulatory restrictions, technological advantages, and access to natural resources.Īrtificial barriers are barriers imposed by government. There are certainly economies of scale, but perhaps the greatest barrier is brand loyalty. It would take years of extensive marketing for customers to accept the viability of a new make of car. Clearly, a large capital investment is required. Establishing product differentiation or brand loyalty may be another very expensive endeavor. It is very difficult to price aggressively when operating at a price disadvantage. New entrants would operate at a cost disadvantage until production is sufficient to take advantage of the economies of scale. This is particularly true when the production process has large economies of scale, meaning a product's average cost decreases as more is produced. Large investments in plant and equipment may be required to get a business started. High start-up costs is the most common barrier to entry. A lemonade stand is a business requiring minimal capital and a readily available market.

At the other extreme are companies with minimal start-up costs and a readily available market. In most countries, electrical utilities are owned by the government, and companies are forbidden to compete with them.
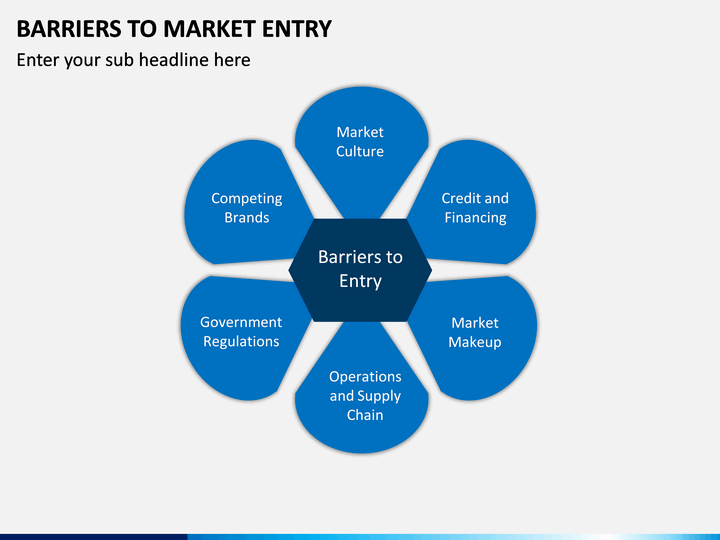
At one extreme is a government mandated monopoly, which forbids other companies from entering the market. Resources must be employed to market and distribute any good or service. Time and money must be invested to produce a good or provide a service. Every business start-up confronts barriers to entry. Barriers to entry may be inherent in an industry (natural barriers to entry), or government imposed (artificial barriers to entry).
Barrier to entry free#
View FREE Lessons! Definition of a Barrier to Entry:Ī barrier to entry is an obstacle that impedes potential competitors from entering an industry.īarriers to entry limit competition.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
